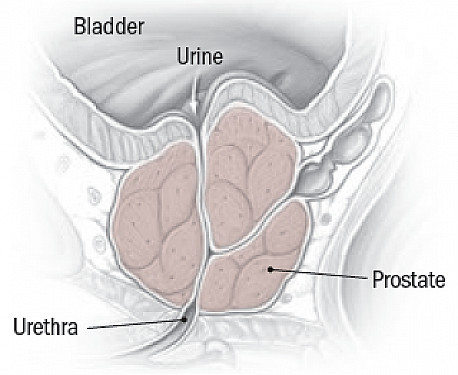
Have you ever wondered where the prostate gland is located in the body? The prostate gland is a small, walnut-sized organ that is located in the lower abdomen of men, between the bladder and the rectum. It plays an important role in producing some of the fluid that makes up semen. Unfortunately, the prostate gland can be prone to a variety of diseases, including prostate cancer, which affects millions of men around the world. In this blog post, we’ll explore where the prostate gland is located in the body and discuss some of the most common diseases of the prostate in men.
The prostate is a small, walnut-shaped gland located just below the bladder in men.
The prostate is a vital part of the male reproductive system. It is responsible for the production of semen, which is the fluid that carries sperm during ejaculation. The prostate also helps to control urine flow. The prostate is a complex organ, made up of several glands and muscle tissue. It is located just below the bladder and surrounded by several layers of tissue. As men age, they may experience problems with their prostate such as an enlarged prostate (also known as benign prostatic hyperplasia or BPH) or prostate cancer. An enlarged prostate can cause difficulty urinating or dribbling, while prostate cancer can be a more serious health concern.
In some cases, adenoma prostate can occur, which is a benign tumor of the prostate. This type of growth often causes no symptoms and typically does not require treatment. However, it should be monitored by a doctor to ensure it does not progress into something more serious. No matter what type of prostate issue you are dealing with, it’s important to talk to your doctor about treatment options that are right for you. Treatment options range from lifestyle changes to medication, and surgery depending on the severity of the condition.
The prostate produces semen, which is the fluid that carries sperm during ejaculation.
The prostate is an essential part of the male reproductive system, as it produces a milky, white fluid called semen. This semen contains sperm cells that are important for fertilization. The production of semen takes place in the adenoma prostate, Where is the prostate gland located just below the bladder. This gland secretes a variety of components that make up the semen, including water, salts, enzymes, fructose, and prostaglandins. During ejaculation, the adenoma prostate contracts and forces the semen out through the urethra. This expulsion of semen carries the sperm cells to the female reproductive system and is necessary for fertilization to occur.
The adenoma prostate is an essential component of the male reproductive system and its proper functioning is essential for reproduction. Therefore, any issue with the prostate can have serious consequences on fertility. In addition, the adenoma prostate can become enlarged or cancerous, and men should seek medical advice if they experience any symptoms or changes in their urinary flow.
The prostate also helps to control urine flow.
Prostate is an important organ in the male reproductive system, as it produces semen and helps to control urine flow. The prostate contains many small glands that produce fluid, known as prostatic fluid, which is released during ejaculation. The size of the prostate can vary significantly between individuals but is typically about the size of a walnut.
Sometimes, the prostate can become enlarged due to a condition known as benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH), also known as an enlarged prostate. This condition occurs when the cells of the prostate gland begin to grow abnormally, leading to a larger size and obstructing the urethra. While BPH does not increase a man’s risk of developing prostate cancer, it can cause uncomfortable urinary symptoms such as frequent urination, weak urine stream, and feeling like you need to urinate again soon after you have finished. In more severe cases, the abnormal cells may form a tumor-like mass, known as an adenoma prostate, which can cause additional issues with urine flow. Treatment for an adenoma prostate typically involves medication or surgery to remove the mass and reduce the risk of complications. In some cases, radiation or other therapies may be recommended as well.




